Subscribe to our Newsletter!
 East Sacramento Preservation
East Sacramento Preservation
Category Archives: Essays
An Insightful article about train tracks and housing: Is this what East Sacramento Wants?
Below is an excellent reprint from Per Square Mile. East Sacramento Preservation is grateful to Per Square Mile, an excellent website about human habitation, and population. The site is written and produced by Tim De Chant. Tim is a senior digital editor at NOVA, journalist, ecologist and creator of Per Square Mile.
Preservation Proximity sans convenience: Houses near train tracks and freeways
March 31, 2011 by Tim De Chant
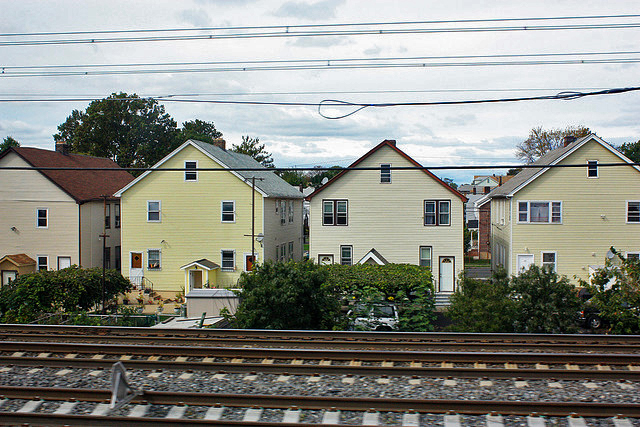
Train tracks and highways are wonderful things. They zip ourselves and our stuff around with unparalleled efficiency. Never has getting anywhere been so easy. They are true marvels of the modern age—unless you can’t use them. Train tracks without nearby stations or those that don’t serve passengers aren’t conveniences, they’re rumbling menaces. And highways without onramps close at hand are roaring headaches. No one wants to live next to them. When transit corridors are nuisances rather than amenities, home prices suffer.
There are a couple of ways to measure how big of a bite nearby-but-inaccessible transit corridors take out of housing prices. One of the simplest is to look at freight trains. Freight trains offer few tangible benefits to the general public, but they present a lot of downsides. Their diesel engines emit low growls, their whistles high pitched wails. Their burdened cars rumble through neighborhoods, shaking doors and windows as they pass. A study conducted in the late 1970s in London, Ontario, found that house prices started dropping off within 800 feet of the tracks. The closer the house, the greater the loss in value.
Another way is to look at freeways without nearby onramps. A study of the Interstate 90 corridor running east from downtown Seattle found that house prices near to the freeway but far from an onramp suffered. A second part of the study focused on the Mt. Baker neighborhood in Seattle, part of which overlies a tunnel for I-90. People who live in Mt. Baker do not have easy access to the freeway, but they also do not suffer from noise or air pollution because of the tunnel. Yet houses dropped in price anyway the closer they were to the tunnel, a fact the study’s authors attributed to stigma of living near a freeway. Houses situated on top of the tunnel were worth 20 percent less than those 300 feet away.
Then there’s the question of commuter or light rail. There are dozens of studies that show living close to a train station increases house prices, but there is such a thing as too close. Apartments in Haifa, Israel, that were within 50 to 100 meters (about 160 to 330 feet) of train tracks sold for 13 percent less than houses outside that buffer. Immediately outside that distance, prices shot up and then tapered off slowly, as those residences were conveniently close to the stations but far enough away from the noise.
One hundred meters is not the universally optimal distance from train tracks, though. Lines with less frequent service may not sufficiently offset the downsides of living next to tracks, and those that run at-grade (as opposed to underground) may drive prices south. For example, houses adjacent to tracks for CalTrain, which offers commuter service to the San Francisco Peninsula, sold for substantially less than houses next to tracks for BART, the light rail system for much of the rest of the Bay Area. The diesel CalTrain runs at-grade and offers less frequent service than the electric BART, large portions of which run underground.
Train tracks and freeways can be a nuisance, and each in their own way. Trains are generally quieter than freeways, but infrequent train passings and whistles at crossings can make them more noticeable. On the other hand, trains produce less pollution than freeways, which have proven negative effects on respiratory health. Living with neither set of problems would be ideal, but modern means of travel are not going away.
Sources:
Kilpatrick, John A., Throupe, Ronald L., Carruthers, John I., & Krause (2007). The Impact of Transit Corridors on Residential Property Values Journal of Real Estate Research, 29 (3), 303-320
Poon, L. (1978). Railway Externalities and Residential Property Prices Land Economics, 54 (2) DOI: 10.2307/3146235
Portnov, Boris A., Genkin, Bella, & Barzilay, Boaz (2009). Investigating the Effect of Train Proximity on Apartment Prices: Haifa, Israel as a Case Study Journal of Real Estate Research, 31(4)
Photo by chrisjbarker.
Posted in Essays
2 Comments
East Sacramento Part of Urban Forest Award
City of Sacramento Named one of the ’10 Best U.S. Cities for Urban Forests’
 The City’s urban forest and its management are one of the best in the U.S., according to a study released in February by the nonprofit group American Forests.
The City’s urban forest and its management are one of the best in the U.S., according to a study released in February by the nonprofit group American Forests.
Through a combination of an in-depth survey, independent data and a vote by a blue-ribbon panel of leading urban forest experts, the nonprofit has named the 10 best U.S. cities for urban forests among the 50 most populous U.S. cities: Austin, Charlotte, Denver, Milwaukee, Minneapolis, New York, Portland, Sacramento, Seattle and Washington, D.C. The list made USA Today.
Joe Benassini is the city’s Urban Forester that oversees policy and planning for the city’s trees. “The story From the City of the Plains to the City of Trees is one of the great tales about how Sacramento’s founders immediately recognized the importance of tree lined streets and began planting an urban forest that is now internationally recognized. “With the help of our own city leaders, the Sacramento Tree Foundation and many others, that legacy continues today,” said Benassini.
“We believe the City’s investments in urban forest resources, including community partnerships, is very worthy of this national recognition by American Forests,” states Ray Tretheway, executive director of the Sacramento Tree Foundation. “The citizens, businesses and many public agencies in Sacramento, particularly the Sacramento Municipal Utility District, value the guidance and commitment of our City’s leadership. Our elected officials and policy makers truly value trees as critical contributors to clean air, summer energy conservation, water quality and the health and well-being of Sacramento’s neighborhoods.”
The project, funded by the U.S. Forest Service, found that while many cities are working to improve their green infrastructure, top-ranked cities, like Sacramento, have made prolonged investments in the health of its urban forest. The City has also benefited from active nonprofit and community participation. Sacramento recognizes that trees don’t just provide aesthetic value; they also help increase property values, reduce energy costs and lower medical costs by improving human health.
The panel recognized Sacramento for its strong volunteer base managed by the Sacramento Tree Foundation with thousands of individuals volunteering thousands of hours of work each year. Another contributing factor for the City’s high ranking is its documented knowledge of its tree canopy, tree species diversity and age class range. In recent years, the City invested in hiring a consultant firm to capture this data. The database includes the characteristics and maintenance history of all of its 100,000 trees on streets and in parks and cemeteries.
Courtesy of Councilmember Cohn’s Newsletter
Posted in Essays
Comments Off on East Sacramento Part of Urban Forest Award
















 Subscribe In A Reader.
Subscribe In A Reader. Check Us Out On Facebook!
Check Us Out On Facebook! Check Us Out On Twitter!
Check Us Out On Twitter! Visit Nextdoor!
Visit Nextdoor!








